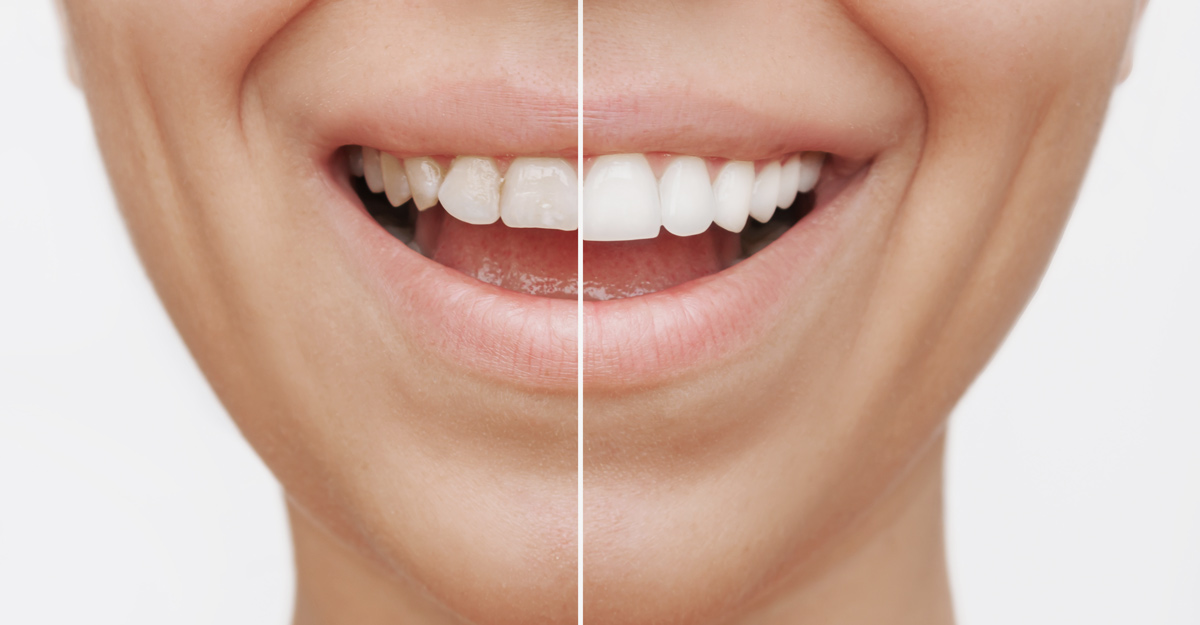
Dental technology is a rapidly advancing field that is transforming the way dental care is delivered across the UK. From the use of computer-aided tools to the fabrication of highly customised dental appliances, modern dentistry is undergoing a digital revolution.
Let’s now take a look at what dental technology is, who is involved in the field, and how these innovations are reshaping patient care.
What is dental technology?
Dental technology encompasses the processes and materials used to create dental appliances that restore teeth or replace missing ones to improve patients’ appearance. These can include crowns, bridges, dentures, dental implants, orthodontic appliances such as braces, and more.
The discipline sits at the intersection of clinical dentistry and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Innovation in dentistry
Traditionally, dental appliances were handcrafted by dental technicians using plaster models and manual tools. While skilled craftsmanship remains vital, technological advances have introduced computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems into dental laboratories.
These systems allow the creation of highly accurate dental devices from digital scans, enhancing precision and reducing errors. The ongoing integration of digital workflows and 3D printing technologies is continuously pushing the boundaries of what dental technology can achieve.
The role of dental technicians
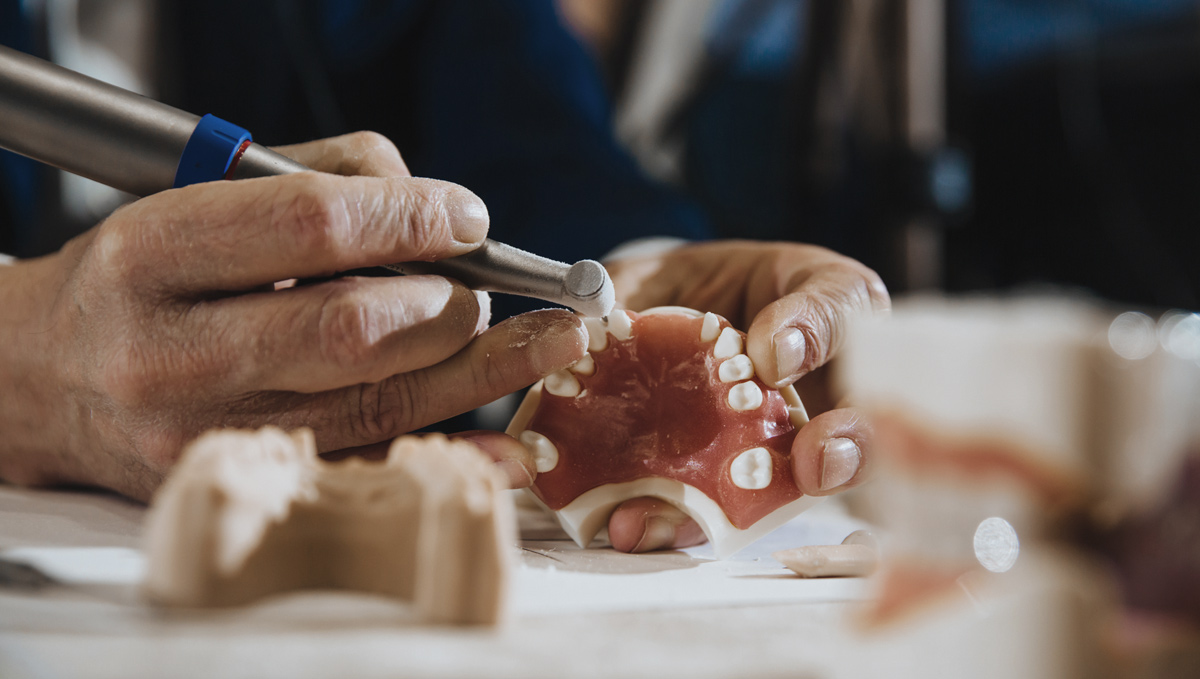
Dental technicians are the experts behind the scenes who bring dental prescriptions to life. They use their knowledge of materials and dental anatomy to produce custom-made dental appliances for individual patients.
Behind the scenes: who are dental technicians?
A dental technician is a healthcare scientist specialising in fabricating crowns, bridges, partial dentures, orthodontic appliances, and other dental devices. They often work in commercial dental laboratories or private practices and may operate their own laboratory.
In the UK, dental technicians must be registered with the General Dental Council (GDC) to practise legally. Some dental technicians undergo further training to become clinical dental technicians, allowing them to work directly with patients, particularly in fitting dentures and providing removable prostheses.
Collaboration between technicians and dentists
Dental technicians work primarily from dental impressions and prescriptions issued by a dentist or dental clinician. The dental clinician assesses the patient’s oral health, takes impressions, and defines treatment goals.
The technician then fabricates the device to the exact specifications, ensuring proper fit, function, and appearance. This close collaboration is essential to provide high-quality dental appliances that meet the patient’s needs and requirements.
Digital dentistry explained
Digital dentistry is the use of technology to improve diagnosis, treatment planning, and dental appliance production.
What is digital dentistry?
Digital dentistry utilises intraoral scanners, 3D imaging, CAD/CAM software, and other specialised equipment to streamline the treatment process. Instead of traditional dental impressions, dentists can use digital scanners to capture precise images of a patient’s teeth and gums.
These images are then transferred to a dental laboratory where computer-aided manufacturing produces the required appliances.
Key tools in digital dental practices
Among the most significant tools are intraoral scanners, which replace uncomfortable dental impressions with quick digital scans.
Computer-aided design allows dental technologists to model devices such as crowns, bridges, and orthodontic appliances virtually before production.
Computer-aided manufacturing uses milling machines or 3D printers to fabricate these designs from metal, ceramic, or plastic materials with exceptional accuracy and repeatability.
3D printing and its applications in dentistry
3D printing technology is increasingly adopted in dental laboratories to enhance the fabrication process.
Creating crowns, bridges, and aligners
Using additive manufacturing, dental labs can print crowns, bridges, and removable orthodontic appliances layer by layer. This technology allows complex geometries that were difficult or impossible to make with traditional methods.
For example, clear aligners and custom trays are now routinely 3D printed to provide a better fit and comfort.
Benefits of additive manufacturing in dental labs
3D printing reduces waste compared to subtractive milling techniques and allows rapid prototyping. This makes it cost-effective, particularly for producing partial dentures and removable prostheses.
Moreover, 3D printing supports advanced dental technology work by facilitating the creation of maxillofacial prostheses and other specialised devices used in reconstructive science.
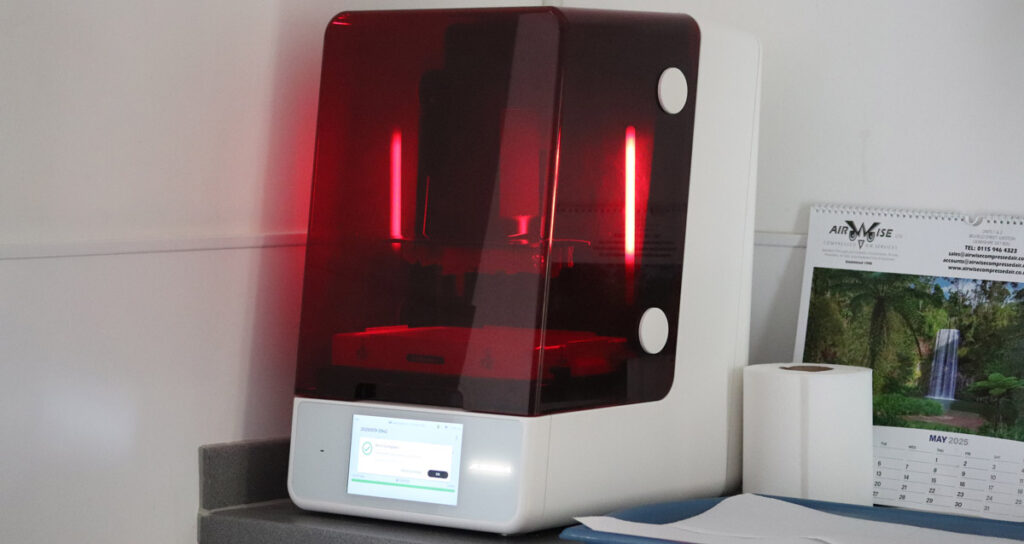
CAD/CAM systems in modern practice
CAD/CAM is a cornerstone of modern dental technology, revolutionising how restorations are designed and fabricated.
How CAD/CAM works in dental design
Dental technicians and clinicians use CAD software to design dental devices digitally, working from patient scans or impressions. The digital file is then sent to CAM machinery, which mills or prints the restoration from solid blocks of ceramic, metal, or composite resin.
This technology is commonly employed for making crowns, bridges, and fixed prostheses with exceptional precision.
Speed and accuracy improvements in restorative work
By automating much of the fabrication process, CAD/CAM reduces human error and shortens production times.
Patients benefit from shorter treatment cycles and improved fitting dental appliances that closely mimic the function and appearance of natural teeth. Dental clinicians can also analyse quality in real-time, ensuring optimal outcomes.
Intraoral scanners and imaging advancements
Intraoral scanners are a major technological leap, replacing traditional impressions and enhancing diagnostics.
Replacing traditional impressions
Conventional dental impressions involve placing trays filled with impression material in a patient’s mouth, which many find uncomfortable. Intraoral scanners capture detailed 3D images of the patient’s mouth quickly and non-invasively, eliminating this discomfort and the risk of errors that moulds are susceptible to, such as bubbles or distortions.
Enhancing patient comfort and diagnosis
These scanners not only improve patient comfort but also provide dentists with instant, highly accurate digital impressions. This facilitates better diagnosis and enables fitting braces to straighten teeth or bonded retainers with greater precision. The high-quality data ensures that dental technicians can produce perfectly fitting orthodontic appliances and dental devices tailored to individual patients.
Artificial intelligence in dentistry
AI is starting to transform diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient management.
AI in diagnostic tools and treatment planning
Artificial intelligence can analyse vast amounts of imaging data rapidly, assisting dentists and orthodontic therapists in detecting early signs of decay, gum disease, or misalignment. AI algorithms can also support treatment planning by simulating outcomes and predicting the effectiveness of orthodontic or implant treatments.
Ethical considerations and patient data
With increasing digitalisation, maintaining patient confidentiality and adhering to data protection regulations is paramount. Healthcare scientists specialising in dental technology must ensure AI tools are used responsibly, respecting patient privacy while improving oral health outcomes.
The rise of teledentistry
Teledentistry is making dental care more accessible and convenient for many patients.
Virtual consultations and remote monitoring
Patients can now receive consultations and follow-ups via video conferencing platforms, which is especially useful for those living in remote areas or those with limited mobility who may not be able to get to the dentist easily. Dentists can assess symptoms, review progress, and provide advice without the patient needing to visit the surgery physically.
Accessibility and convenience for patients
Teledentistry supports ongoing monitoring of dental appliances such as removable orthodontic appliances or dental braces. It also helps dental clinicians maintain direct contact with patients to ensure the patient’s general dental welfare is upheld between appointments.
Impact on patient experience
Advances in dental technology are improving treatment comfort, speed, and results.
Shorter treatment times and less invasive procedures
Digital workflows allow dental clinicians to deliver treatments such as dental implants and crown and bridge restorations more efficiently. Same-day crowns fabricated with CAD/CAM reduce the need for multiple appointments. Minimally invasive orthodontic treatments with plastic or metal devices like braces to straighten teeth have become more discreet and comfortable.
Personalised treatment plans and better communication
The ability to produce digital models and visual simulations enables clinicians to involve patients in their care decisions. Patients can see how dental braces, bonded retainers, or partial dentures will affect their appearance before treatment begins, increasing satisfaction and compliance.
The future of dental technology
Dental technology will continue to evolve, requiring skilled professionals and ongoing education.
Emerging innovations on the horizon
Future advancements may include nanotechnology to improve biomaterials, smart dental devices that monitor oral health in real-time, and enhanced 3D printing capabilities. These will further push the boundaries of reconstructive science, leading to even more precise dental appliances.
Preparing the dental workforce for technological change
To keep pace, those looking to become a dental technician are encouraged to study dental technology through foundation degrees, obtain a degree in dental technology, or go through the NHS Scientist Training Programme.
The trainee dental technician role is essential for practical experience, allowing individuals to train students and acquire specific clinical training.
Equally, dental technologists must adhere to strict quality control and safety practices, including wearing protective clothing and maintaining clean laboratory environments.
GoDigital Dental: a trusted digital dental laboratory
At GoDigital Dental, we take pride in delivering precision-crafted dental appliances to practices throughout the UK. Our team of highly trained dental technicians combines advanced dental technology with expert craftsmanship to produce crowns, bridges, implants, and other restorations that meet the highest clinical standards.
We work closely with dental clinicians to ensure every appliance is tailored to the individual patient, using digital workflows, CAD/CAM systems, and 3D printing for accuracy and efficiency.
Whether you are part of a private practice or the NHS, GoDigital Dental is committed to supporting your work with dependable service, fast turnaround times, and a dedication to innovation in modern dentistry.