Dental technicians have an important role in modern dentistry, working behind the scenes to make sure patients get high-quality dental appliances and restorations. From fixed prosthesis to dental braces and crowns, the work of a dental technician affects patients’ oral health, comfort, and appearance.
With the rise of digital dentistry and advanced dental technology, the role has evolved significantly, requiring a combination of manual dexterity, technical expertise, and collaboration with the wider healthcare team.
Understanding the role of a dental technician
Definition and overview of a dental technician
A dental technician is a healthcare professional who designs, makes, and repairs dental devices and appliances. They work closely with dentists, prosthodontic technicians, and the wider dental team to create custom solutions for individual patients. Their work can include crowns, bridges, fixed restorations, dental implants, and dental braces, all made to improve patients’ appearance and oral function.
Some dental technicians also specialise in maxillofacial prosthetics, reconstructive sciences, or conservation techniques, helping patients who require complex restorative care. Clinical dental technicians can work directly with patients in community dental services or dental hospitals, providing solutions for missing teeth or other oral issues while supporting the dentist and wider healthcare team.
The evolving role in the era of digital dentistry
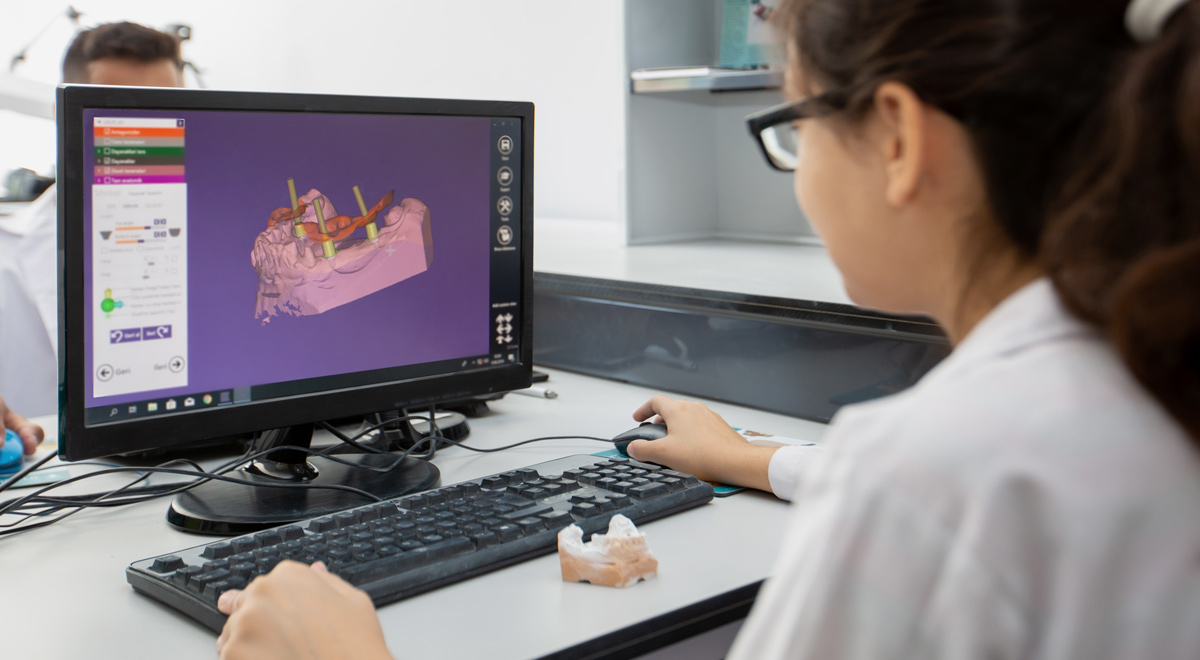
Digital dentistry has changed the work of dental technicians, bringing computer-aided design, 3D printing, and milling machines into commercial dental laboratories. Dental technicians now use traditional skills along with advanced digital workflows to make dental appliances more accurate, efficient, and high-quality.
This digital approach lets technicians fine-tune restorations, adjust tooth positions, and make devices that fit well in a patient’s mouth. As dental technology keeps improving, dental technicians need ongoing professional development and further training to stay skilled in specialist areas like prosthodontics or orthodontics.
Types of dental technicians in modern practice
Crown and bridge technicians
Crown and bridge technicians specialise in designing and fabricating fixed restorations, including crowns, bridges, and implants. They work with dentists to ensure that each restoration matches the patient’s natural teeth in colour, shape, and alignment.
Quality control is essential, as crowns and bridges must withstand daily use while improving patients’ appearance. These technicians often work in commercial laboratories or operate their own laboratory, using specialised equipment to achieve precise results.
Orthodontic and implant restoration technicians
Orthodontic and implant restoration technicians work on devices that straighten teeth or replace missing teeth. Orthodontic technicians make dental braces and other orthodontic appliances, carefully adjusting tooth positions to get the best alignment.
Implant technicians work on dental implants and fixed prosthesis to restore both function and appearance. Both roles need strong reasoning skills, attention to detail, and the ability to communicate effectively with dentists and the wider healthcare team.
Core responsibilities in a digital lab
Designing and fabricating restorations using digital tools
Modern dental technicians use computer-aided design software to make detailed 3D models of crowns, bridges, and prostheses. Digital workflows let technicians adjust tooth positions, fine-tune dental devices, and check how restorations will fit in a patient’s mouth.
The use of specialised equipment, such as milling machines and 3D printers, ensures that dental appliances are precise, durable, and comfortable. This level of precision supports clinical dental technicians in providing patients with customised solutions that improve both oral function and appearance.
Collaborating with dentists and digital workflow specialists
Dental technicians work directly with dentists, orthodontists, and other members of the dental team to make sure each restoration or device meets clinical requirements. Communication is important in a partnership, as technicians need to understand treatment plans, patient preferences, and functional needs.
Within clinical settings, dental technicians often help in community dental services or dental hospitals, supporting treatment planning and assisting dentists while patients are having dental work. Working closely with the wider healthcare team gives technicians insight into patient care and ensures dental appliances meet professional standards.

Digital technical skills required
CAD/CAM software proficiency
Proficiency in computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) is very important for modern dental technicians. CAD/CAM software lets technicians design crowns, bridges, and dental implants with accuracy and precision.
Knowing how to turn digital models into physical restorations allows technicians to make devices that fit perfectly in a patient’s mouth while keeping high aesthetic standards. These skills are now often expected in commercial laboratories and dental schools, especially for trainee dental technicians completing a diploma in dental technology or a degree in dental technology.
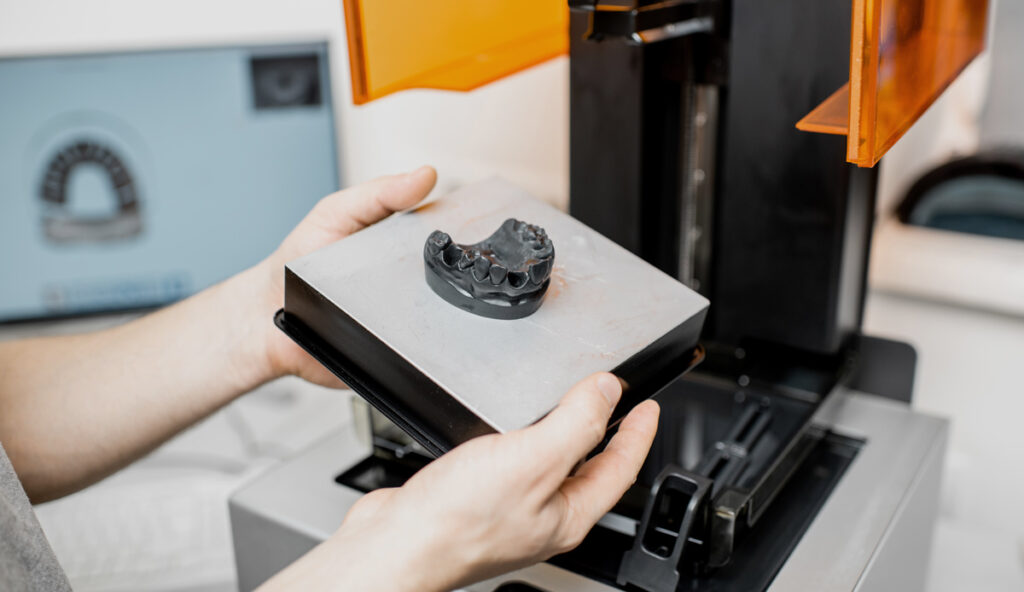
3D printing, milling, and digital scanning techniques
Knowledge of digital scanning and 3D printing technology is increasingly required in both commercial laboratories and dental hospitals. Dental technicians use scanners to capture precise impressions of a patient’s teeth and jaws, and then produce restorations using 3D printers or milling machines.
These techniques improve efficiency, reduce errors, and allow for rapid production of dental appliances, supporting patients who need immediate solutions for missing teeth or dental braces. Digital workflows also help technicians work more effectively with the wider healthcare team and complete treatments with a higher level of precision.
Traditional skills still relevant in a digital lab
Material knowledge and precision crafting
Even with digital workflows, dental technicians still need a strong understanding of dental materials, including ceramics, metals, and composite resins. Knowing how different materials behave and react under pressure is key to making durable crowns, bridges, and fixed prostheses.
Manual dexterity and careful handling are still very important, especially when technicians fine-tune restorations or make dental devices to meet strict quality control standards. These skills support digital workflows and keep patients safe and comfortable.
Attention to detail and manual dexterity
Manual dexterity and reasoning skills are vital for all dental technicians. Many training programmes include a manual dexterity test to assess a trainee dental technician’s suitability for the profession. Technicians must consistently work with precision, whether carving crowns, adjusting dental braces, or shaping prostheses.
Protective clothing and careful handling of specialised equipment ensure safety while producing high-quality results. Attention to detail also supports the production of complex devices such as maxillofacial prosthetics, allowing patients to regain oral function and improve their appearance.
Tools and technology in a digital dental lab
Intraoral and desktop scanners
Intraoral scanners are used to capture detailed digital impressions of a patient’s teeth and soft tissues, replacing traditional moulds. Desktop scanners convert physical impressions into digital models for further design and modification.
These tools are critical for dental technologists who work in commercial laboratories or operate their own laboratory, enabling them to create custom restorations with speed and accuracy. Accurate scans also help technicians support clinical dental technicians in direct contact with patients during treatment.
Milling machines, 3D printers, and digital design software
Milling machines and 3D printers allow dental technicians to produce crowns, bridges, dental implants, and orthodontic devices with precision. Digital design software integrates seamlessly with these machines, enabling technicians to simulate the fit of a device in a patient’s mouth and make adjustments before fabrication.
Specialised equipment also supports the production of maxillofacial prosthetics and other complex reconstructions, improving patients’ appearance and oral function. This combination of digital tools and manual skills ensures dental devices meet professional standards and patient expectations.
Career path and future opportunities
Digital dentistry training, qualifications, and accreditation in the UK
Becoming a dental technician requires completing recognised training programmes, such as a diploma in Dental Technology, a foundation degree, a Dental Technician Level 5 Higher Apprenticeship, or a BSc Hons in Dental Technology. Trainee dental technicians usually begin in commercial laboratories or dental hospitals, getting hands-on experience while working under supervision.
Professional development is supported by membership of a professional body and registration with the General Dental Council. Additional postgraduate training and further training courses are available for those who wish to specialise in areas such as prosthodontic work, orthodontics, or maxillofacial prosthetics.
Emerging specialisations and career growth in digital dental technology
Opportunities for dental technicians continue to expand with advances in digital dentistry. Clinical dental technicians may work directly with patients in community dental services, providing fixed restorations, dental braces, and dental implants. Conservation technicians, prosthodontic technicians, and healthcare scientists contribute to specialised areas such as reconstructive sciences and maxillofacial prosthetics.
Dental technicians can progress to running their own dental laboratory, supervising teams in commercial laboratories, or taking on teaching roles in dental schools and degree courses. Continuous professional development, access to specialised equipment, and training in digital techniques ensure that dental technologists remain at the forefront of dentistry while supporting the wider healthcare team.
Let our expert team at GoDigital Dental take care of your digital dentistry needs!
At GoDigital Dental, our experienced team combines years of expertise with advanced digital dentistry technology. Using CAD/CAM design, 3D printing, and digital workflows, we create precise dental appliances, crowns, bridges, implants, and orthodontic devices that fit perfectly in the patient’s mouth and complement their natural teeth. Working closely with dentists and the wider healthcare team, we provide tailored solutions that support both clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
We ensure seamless communication throughout the dental laboratory process, from digital impressions to implant planning and shade taking. Whether you are a dentist seeking a commercial laboratory partner or direct contact with clinical dental technicians, GoDigital Dental offers specialised equipment, expertise, and professional development to complete every case to the highest standard. Let our team take care of your digital dentistry needs.
FAQs
What skills are most important for a dental technician?
Dental technicians need a mix of practical and technical skills to do their job well. Manual dexterity is essential, as they work with small dental devices like crowns, bridges, dental implants, and dental braces. Attention to detail ensures each dental appliance fits properly and meets quality standards. Reasoning skills help technicians understand treatment plans and make adjustments. Knowledge of dental materials, such as ceramics, metals, and composite resins, is also very important.
Communication is needed to work with dentists, orthodontists, and the wider dental team. Digital skills, including 3D printing and CAD/CAM, allow dental technicians to produce accurate, high-quality dental appliances efficiently.
Is ongoing training important for dental technicians?
Ongoing training is very important for dental technicians to keep up with changes in dentistry and dental technology. New materials, techniques, and treatment approaches require updated skills. Regular professional development helps technicians maintain high standards when making crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and other dental appliances.
Further training also allows dental technicians to specialise in areas such as prosthodontics, orthodontics, or maxillofacial prosthetics. It helps them work more effectively with dentists and the wider healthcare team, ensuring restorations fit accurately, meet quality control standards, and improve patients’ oral health and appearance. Continuous learning also helps technicians stay confident and skilled in their work.
How do dental technicians ensure quality and accuracy?
Dental technicians ensure quality and accuracy by following strict procedures at every stage of making dental appliances. They carefully measure, shape, and fit crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and other restorations. Attention to detail and manual dexterity are essential, as even small errors can affect the fit and function of a dental device. Regular checks and adjustments help technicians maintain high standards.
Quality control is supported by close communication with dentists and the wider healthcare team. Dental technicians also use tests and inspections to make sure each restoration matches the patient’s needs and improves both comfort and appearance.
Do dental technicians work directly with patients?
Dental technicians sometimes work directly with patients, especially clinical dental technicians who provide solutions for missing teeth and other dental needs. They take impressions, fit dental appliances, and make adjustments to ensure crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and other devices are comfortable and effective. Working directly allows technicians to see how dental devices fit in the patient’s mouth and make changes as needed.
Even when not in direct contact, dental technicians work closely with dentists and the wider healthcare team. This collaboration ensures each restoration meets clinical requirements, fits accurately, and improves patients’ oral health, function, and appearance.
Are dental technicians in demand right now?
Dental technicians are in demand as modern dentistry continues to grow and evolve. Dental practices, commercial laboratories, and dental hospitals need skilled technicians to create crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and other dental appliances. The need for high-quality restorations and fixed prosthesis ensures that technicians with strong skills and attention to detail remain essential.
Digital dentistry and new dental technology have increased opportunities for technicians to specialise in areas such as prosthodontics, orthodontics, and maxillofacial prosthetics. Trainee dental technicians and experienced dental technologists who complete recognised training programmes or professional development are highly sought after by dentists and the wider healthcare team.
Is the job creative, technical, or both?
The job of a dental technician is both creative and technical. Technicians need technical skills to design and make crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and other dental appliances that fit accurately and meet clinical standards. Knowledge of dental materials, precision, and attention to detail are essential to ensure restorations are functional and durable.
At the same time, creativity is important to make dental devices look natural and match the patient’s teeth. Dental technicians use their artistic skills to shape, colour, and fine-tune restorations, helping to improve patients’ appearance while working closely with dentists and the wider healthcare team.
What tools, materials, and technologies do dental technicians use?
Dental technicians use a wide range of tools, materials, and technologies to create dental appliances. They work with hand tools, specialised equipment, and protective clothing to shape and finish crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and other dental devices. Knowledge of dental materials, such as ceramics, metals, and composite resins, is essential to ensure restorations are durable and functional.
Technologies in dental laboratories include digital workflows, scanners, and milling machines to produce accurate restorations. Technicians also use quality control checks and testing equipment to make sure each device fits correctly and meets professional standards, supporting dentists and the wider healthcare team.
How does a dental technician stay up to date with new materials and technology?
Dental technicians stay up to date with new materials and technology through ongoing professional development and further training. They attend courses, workshops, and training programmes to learn about the latest dental appliances, crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and fixed prosthesis. Keeping up with changes in dental materials, techniques, and restorative methods ensures that technicians can produce high-quality restorations that meet patient needs.
Technicians also read industry publications, join professional bodies, and share knowledge with the wider healthcare team. Staying informed helps them maintain quality, improve patient outcomes, and use modern tools and equipment effectively in commercial laboratories or dental hospitals.
Do I have to register with a professional body, and what does that involve?
In the UK, dental technicians must be registered with the General Dental Council (GDC) to work legally and use protected titles like “dental technician.” It is a criminal offence to offer dental services or use the title if unregistered.
Registration involves meeting the GDC’s standards for training, skills, and professional conduct. Dental technicians also need recognised qualifications, such as a diploma in dental technology, a foundation degree, or a BSc Hons in dental technology. Being registered ensures technicians can work safely and legally, produce high-quality dental appliances, and collaborate confidently with dentists and the wider healthcare team.
What are the biggest challenges of being a dental technician?
Being a dental technician comes with several challenges, including the need for high precision and attention to detail. Creating crowns, bridges, dental implants, dental braces, and other dental appliances requires manual dexterity and careful handling of dental materials. Small mistakes can affect fit, function, and patient comfort, so technicians must work accurately under pressure.
Another challenge is keeping up with new dental technology, materials, and techniques. Ongoing professional development and further training are essential. Dental technicians also need to communicate effectively with dentists and the wider healthcare team to ensure restorations meet clinical standards and improve patients’ oral health and appearance.